 Hypertension, commonly known as high blood pressure, is a prevalent health condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide. Often referred to as the “silent killer,” hypertension typically presents no symptoms, making it difficult for individuals to recognize its presence until serious health complications arise. This article delves into the intricacies of hypertension, exploring its causes, symptoms, risk factors, diagnosis, treatment options, and preventive measures.
Hypertension, commonly known as high blood pressure, is a prevalent health condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide. Often referred to as the “silent killer,” hypertension typically presents no symptoms, making it difficult for individuals to recognize its presence until serious health complications arise. This article delves into the intricacies of hypertension, exploring its causes, symptoms, risk factors, diagnosis, treatment options, and preventive measures.
What is Hypertension?
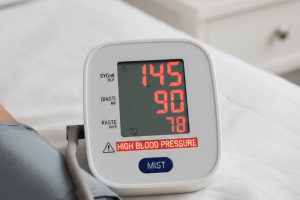
Hypertension is defined as a condition where the force of blood against the walls of the arteries is consistently too high. Blood pressure readings are expressed in millimeters of mercury (mm Hg) and consist of two numbers: systolic pressure (the upper number) and diastolic pressure (the lower number). A reading of 130/80 mm Hg or higher is generally considered indicative of hypertension.
Types of Hypertension
There are two primary types of hypertension:
-
- Primary Hypertension: This form accounts for the majority of cases and typically develops gradually over many years. The exact cause is often unknown, but factors such as genetics, age, and lifestyle choices play a significant role.
- Secondary Hypertension: This type is caused by an underlying condition, such as kidney disease, hormonal disorders, or certain medications. It tends to appear suddenly and can lead to more severe blood pressure elevations.
The Importance of Monitoring Blood Pressure
Regular monitoring of blood pressure is crucial for early detection and management of hypertension. Many individuals remain unaware of their condition, as it often does not present noticeable symptoms. Routine check-ups can help identify elevated blood pressure levels, allowing for timely intervention.
Blood Pressure Categories
Understanding blood pressure categories is essential for recognizing hypertension:
| Blood Pressure Category | Systolic (mm Hg) | Diastolic (mm Hg) |
|---|---|---|
| Normal | Less than 120 | Less than 80 |
| Elevated | 120-129 | Less than 80 |
| Stage 1 Hypertension | 130-139 | 80-89 |
| Stage 2 Hypertension | 140 or higher | 90 or higher |
| Hypertensive Crisis | Higher than 180 | Higher than 120 |
Symptoms of Hypertension
Hypertension is often asymptomatic, which is why it is crucial to have regular check-ups. However, when blood pressure reaches dangerously high levels, individuals may experience symptoms such as:
- Severe headaches
- Shortness of breath
- Nosebleeds
- Dizziness
- Chest pain
These symptoms may indicate a hypertensive crisis, requiring immediate medical attention.
Risk Factors for Hypertension
Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing hypertension. These include:
Modifiable Risk Factors
-
- Obesity: Excess weight can lead to increased blood pressure.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity contributes to weight gain and elevated blood pressure.
- Diet: High sodium intake and low potassium consumption can negatively impact blood pressure levels.
- Alcohol Consumption: Excessive drinking can raise blood pressure.
- Tobacco Use: Smoking damages blood vessels and increases blood pressure.
Non-Modifiable Risk Factors
-
- Age: The risk of hypertension increases with age.
- Family History: A genetic predisposition can elevate the risk of developing hypertension.
- Race: Certain ethnic groups, particularly African Americans, are at a higher risk.
Causes of Hypertension
The causes of hypertension can be complex and multifactorial. While primary hypertension has no identifiable cause, secondary hypertension can result from various medical conditions, including:
- Kidney Disease: Impaired kidney function can lead to fluid retention and increased blood pressure.
- Hormonal Disorders: Conditions such as hyperthyroidism or adrenal gland tumors can elevate blood pressure.
- Sleep Apnea: This disorder can disrupt normal breathing patterns during sleep, leading to increased blood pressure.
Diagnosing Hypertension
Diagnosis of hypertension typically involves measuring blood pressure during routine medical visits. If readings are consistently elevated, further evaluation may be necessary. Healthcare providers may recommend:
- Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring: This involves wearing a portable device that measures blood pressure at regular intervals over 24 hours.
- Blood Tests: These can help identify underlying conditions contributing to hypertension.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): This test assesses heart function and can reveal any abnormalities.
Treatment Options for Hypertension
Managing hypertension often requires a combination of lifestyle changes and medication. Treatment plans are tailored to the individual’s specific needs and may include:
Lifestyle Modifications
-
- Dietary Changes: Adopting a heart-healthy diet, such as the DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet, can significantly lower blood pressure. This diet emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy while reducing sodium intake.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in physical activity for at least 150 minutes per week can help maintain a healthy weight and lower blood pressure.
- Weight Management: Losing even a small amount of weight can have a positive impact on blood pressure levels.
- Stress Reduction: Practicing relaxation techniques, such as yoga or meditation, can help manage stress and lower blood pressure.
Medications
If lifestyle changes alone are insufficient, healthcare providers may prescribe antihypertensive medications. Common classes of medications include:
-
- Diuretics: Help the body eliminate excess sodium and fluid.
- ACE Inhibitors: Relax blood vessels and reduce blood pressure.
- Calcium Channel Blockers: Prevent calcium from entering heart and blood vessel cells, leading to relaxation of blood vessels.
- Beta-Blockers: Reduce heart rate and the workload on the heart.
Complications of Untreated Hypertension
If left unmanaged, hypertension can lead to severe health complications, including:
- Heart Disease: Hypertension is a major risk factor for coronary artery disease and heart failure.
- Stroke: High blood pressure can cause blood vessels in the brain to rupture or become blocked.
- Kidney Damage: Hypertension can impair kidney function, leading to chronic kidney disease.
- Vision Loss: Damage to the blood vessels in the eyes can result in vision impairment.
Preventing Hypertension
Preventing hypertension involves adopting a healthy lifestyle and being proactive about health management. Here are some effective strategies:
- Regular Check-Ups: Routine blood pressure screenings can help catch hypertension early.
- Healthy Eating: Focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains while limiting sodium intake.
- Physical Activity: Aim for regular exercise to maintain a healthy weight and improve cardiovascular health.
- Avoid Tobacco and Limit Alcohol: Quitting smoking and moderating alcohol consumption can significantly reduce the risk of hypertension.
Hypertension is a widespread health issue that requires attention and management. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and risk factors is crucial for prevention and treatment. By adopting a healthy lifestyle and seeking regular medical care, individuals can effectively manage their blood pressure and reduce the risk of serious health complications. Awareness and education about hypertension are vital in combating this silent killer and promoting overall health and well-being.
Our Medical Memberships Cover High Blood Pressure Treatment
Direct Primary Care (DPC) is a model of care where the patient pays an upfront monthly membership fee for high-quality and low-cost primary care. This means no surprise fees or being billed differently for sick visits versus wellness visits. This model is accessible to all. The focus of Direct Primary Care is ongoing wellness and prevention to prevent unnecessary hospitalizations or costly visits to the ER for primary care services.
> Learn More About Our Medical Memberships
Contact Us (727-312-1262) To Learn More!
—
 About Honeybee Holistic Health
About Honeybee Holistic Health
Honeybee Holistic Health strongly believes in a holistic, organic, and integrative model of care where the patient is the center of all decisions. Our approach is to empower each one of our patients to heal themselves and to make informed, autonomous decisions in their plan of care. This is approached by integrating modern medicine with well-studied homeopathic treatment options when appropriate.
> Learn More