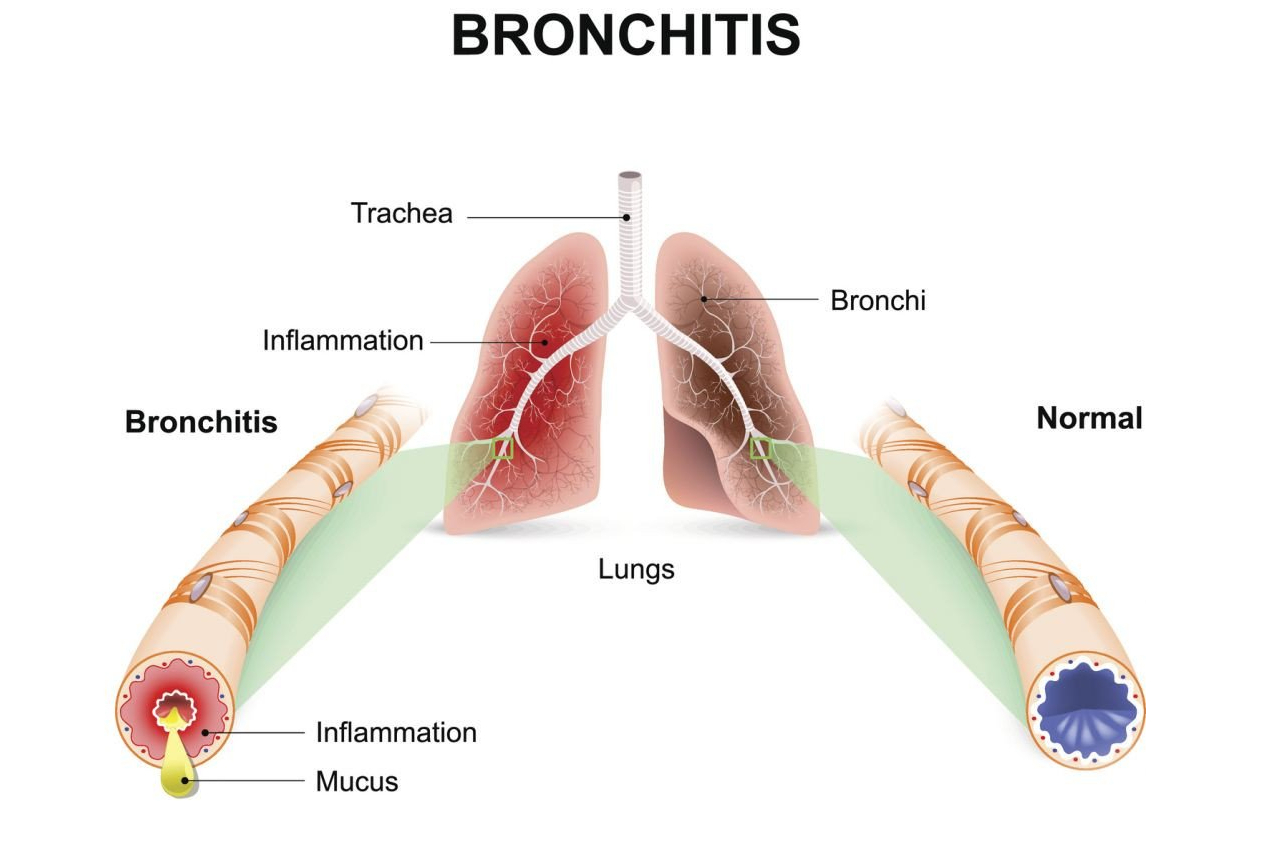
What is Bronchitis?
Bronchitis is an inflammatory condition that targets the bronchial tubes, the airways that connect the nose and mouth to the lungs. When these tubes become irritated and swollen, they produce excess mucus, leading to a persistent cough and other respiratory symptoms. Bronchitis can be categorized into two main types: acute and chronic.
Acute Bronchitis
Acute bronchitis is a temporary condition that typically develops as a result of a viral or bacterial infection, often following a cold or the flu. The symptoms of acute bronchitis usually resolve within a few weeks, although the cough may linger for several more weeks as the airways heal.
Chronic Bronchitis
In contrast, chronic bronchitis is a more serious and long-lasting condition that is classified as a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Characterized by a persistent cough that produces mucus, chronic bronchitis is often caused by long-term exposure to irritants, such as cigarette smoke or air pollution. Unlike acute bronchitis, chronic bronchitis never truly goes away and requires ongoing management.
Symptoms of Bronchitis
The primary symptom of both acute and chronic bronchitis is a persistent, productive cough that may bring up mucus or phlegm. Other common symptoms include:
- Wheezing or a whistling sound when breathing
- Chest discomfort or tightness
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Low-grade fever
- Chills and body aches
In acute bronchitis, these symptoms typically appear suddenly and may be accompanied by a runny nose, sore throat, and headaches. Chronic bronchitis, on the other hand, is characterized by a cough that lasts for at least three months, with recurring episodes over the course of two consecutive years.
Differentiating Bronchitis from Other Respiratory Conditions
It’s important to note that a persistent cough can be a symptom of various respiratory conditions, not just bronchitis. Conditions like asthma, pneumonia, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) can also cause similar symptoms, making it crucial to seek medical attention for an accurate diagnosis.
Causes of Bronchitis
The primary causes of bronchitis can be divided into two main categories: infectious and non-infectious.
Infectious Causes
Viruses are the most common cause of acute bronchitis, with the same viruses that trigger the common cold or influenza often responsible. Bacterial infections, such as those caused by Bordetella pertussis, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, or Chlamydia pneumoniae, can also lead to acute bronchitis in some cases.
Non-Infectious Causes
Chronic bronchitis is primarily caused by long-term exposure to irritants, with cigarette smoke being the most significant contributor. Other potential non-infectious causes include:
-
- Air pollution
- Dust or chemical fumes
- Repeated episodes of acute bronchitis
- Underlying conditions like asthma or GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease)
Risk Factors for Bronchitis
Certain factors can increase an individual’s risk of developing either acute or chronic bronchitis:
- Smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke
- Weakened immune system (e.g., in older adults, infants, or those with chronic illnesses)
- Asthma or allergies
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
- Exposure to air pollutants or irritants in the workplace
Understanding these risk factors can help individuals take proactive steps to prevent or manage their bronchitis.
Diagnosis of Bronchitis
Diagnosing bronchitis typically involves a combination of a physical examination, medical history, and various diagnostic tests.
Physical Examination
During the initial consultation, your healthcare provider will perform a physical examination, using a stethoscope to listen for abnormal sounds in your lungs, such as wheezing or crackling. They may also ask about your symptoms, including the duration and characteristics of your cough.
Diagnostic Tests
Depending on the suspected type of bronchitis and the need to rule out other conditions, your healthcare provider may order one or more of the following diagnostic tests:
-
- Chest X-ray: This imaging test can help identify signs of pneumonia or other underlying lung conditions.
- Sputum test: Analysis of the mucus (sputum) you cough up can help detect the presence of bacteria or viruses.
- Pulmonary function tests: These breathing tests, such as spirometry, measure how well your lungs are functioning and can help distinguish between bronchitis and conditions like asthma or COPD.
- Blood tests: Blood work can provide information about the presence of infections or other underlying health issues.
- Nasal swab: If COVID-19 or other respiratory viruses are suspected, a nasal swab may be taken for testing.
By combining the physical examination and diagnostic tests, your healthcare provider can determine the specific type of bronchitis you are experiencing and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Treatment of Bronchitis
The treatment approach for bronchitis depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition.
Acute Bronchitis Treatment
In most cases of acute bronchitis, the condition resolves on its own within a few weeks, and treatment primarily focuses on managing the symptoms. Common treatment approaches include:
-
- Rest and fluids: Getting plenty of rest and staying hydrated can help the body’s natural healing process.
- Over-the-counter medications: Cough suppressants, pain relievers, and decongestants can provide symptomatic relief.
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics are rarely prescribed for acute bronchitis, as the majority of cases are caused by viruses. However, if a bacterial infection is suspected, your healthcare provider may recommend a course of antibiotics.
- Inhaled medications: If you have underlying conditions like asthma or COPD, your healthcare provider may prescribe bronchodilators or corticosteroids to help open your airways and reduce inflammation.
Chronic Bronchitis Treatment
The management of chronic bronchitis typically involves a combination of lifestyle changes and medical interventions, with the primary goals of reducing symptoms, preventing exacerbations, and slowing the progression of the disease.
-
- Smoking cessation: Quitting smoking is the most important step in managing chronic bronchitis, as it can help prevent further damage to the lungs and improve overall respiratory health.
- Medications: Your healthcare provider may prescribe a variety of medications, including bronchodilators, corticosteroids, and mucolytics (to thin mucus), to help manage your symptoms and improve lung function.
- Oxygen therapy: For individuals with severe chronic bronchitis, supplemental oxygen may be necessary to maintain adequate oxygen levels in the blood.
- Pulmonary rehabilitation: This comprehensive program, which includes exercise, education, and counseling, can help improve your breathing, physical function, and overall quality of life.
- Lung transplant: In some cases, individuals with end-stage chronic bronchitis may be candidates for a lung transplant, which can significantly improve their prognosis.
Preventing Bronchitis
While it’s not always possible to prevent bronchitis, there are several steps you can take to reduce your risk:
- Quit smoking and avoid secondhand smoke: Smoking is a major risk factor for both acute and chronic bronchitis, so quitting or avoiding exposure to tobacco smoke is crucial.
- Get vaccinated: Annual flu shots and pneumonia vaccines can help protect you from the viruses that commonly cause acute bronchitis.
- Wash your hands frequently: Proper hand hygiene can help prevent the spread of viral and bacterial infections that can lead to bronchitis.
- Wear a mask: Wearing a mask can help protect your lungs from airborne irritants and pollutants that can trigger or exacerbate bronchitis.
- Manage underlying conditions: If you have asthma, COPD, or GERD, work closely with your healthcare provider to keep these conditions under control and reduce your risk of developing bronchitis.
Outlook and Prognosis
The prognosis for individuals with bronchitis can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition.
Acute Bronchitis
In most cases, acute bronchitis resolves within a few weeks, and the long-term outlook is generally good. However, in some instances, acute bronchitis can lead to more serious complications, such as pneumonia, especially in individuals with weakened immune systems or underlying respiratory conditions.
Chronic Bronchitis
The prognosis for chronic bronchitis is more guarded, as it is a lifelong condition that can progressively worsen over time. Individuals with chronic bronchitis are at an increased risk of developing other COPD-related complications, such as emphysema, and may experience more frequent exacerbations that can further impair their respiratory function. Timely diagnosis, adherence to treatment, and lifestyle modifications can help slow the progression of chronic bronchitis and improve the overall quality of life.
Our Medical Memberships Cover Bronchitis Diagnosis and Treatment
Direct Primary Care (DPC) is a model of care where the patient pays an upfront monthly membership fee for high-quality and low-cost primary care. This means no surprise fees or being billed differently for sick visits versus wellness visits. This model is accessible to all. The focus of Direct Primary Care is ongoing wellness and prevention to prevent unnecessary hospitalizations or costly visits to the ER for primary care services.
> Learn More About Our Medical Memberships
Bronchitis, whether acute or chronic, is a respiratory condition that can significantly impact an individual’s daily life. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and risk factors associated with bronchitis, as well as the available treatment options and preventive measures, individuals can take a proactive approach to managing this condition and maintaining their respiratory health. Regular communication with healthcare providers and a commitment to making lifestyle changes can be instrumental in effectively managing bronchitis and improving long-term outcomes.
Contact Us (727-312-1262) To Learn More!
—
 About Honeybee Holistic Health
About Honeybee Holistic Health
Honeybee Holistic Health strongly believes in a holistic, organic, and integrative model of care where the patient is the center of all decisions. Our approach is to empower each one of our patients to heal themselves and to make informed, autonomous decisions in their plan of care. This is approached by integrating modern medicine with well-studied homeopathic treatment options when appropriate.
> Learn More