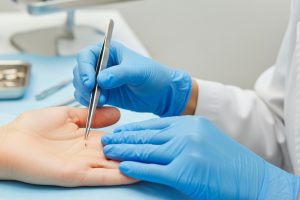
 Foreign body removal is a common procedure performed in general medical offices, addressing a variety of situations where objects become lodged in different parts of the body. This article explores the types of foreign body removal typically conducted in a general medical office, the methods employed, and the importance of timely intervention.
Foreign body removal is a common procedure performed in general medical offices, addressing a variety of situations where objects become lodged in different parts of the body. This article explores the types of foreign body removal typically conducted in a general medical office, the methods employed, and the importance of timely intervention.
Types of Foreign Bodies Encountered
Common Locations for Foreign Bodies
Foreign bodies can be found in various locations within the human body, with the most frequent sites being the ears, nose, throat, and occasionally the eyes. Each location presents unique challenges and requires specific techniques for safe removal.
-
- Ears: Common objects include small toys, beads, and insects. Adults may also experience foreign bodies like cotton swabs or pieces of earplugs.
- Nose: Children are particularly prone to inserting items such as beads, buttons, or food into their nostrils.
- Throat: Objects like coins, bones, and small toys can become lodged in the throat, posing a risk of choking.
- Eyes: Foreign bodies in the eye can include dust, metal shards, or small insects, necessitating careful handling to avoid damage.
Demographics Affected
While foreign body incidents can occur in individuals of all ages, children are the most commonly affected group, accounting for a significant percentage of cases. Adults, particularly those with certain medical conditions or cognitive impairments, may also require foreign body removal.
Symptoms Indicating Foreign Body Presence
Recognizing Signs in Different Areas
Identifying the presence of a foreign body can be challenging, as symptoms may vary based on the location and type of object involved.
-
- Ear Symptoms: Patients may experience pain, decreased hearing, or a sensation of fullness in the ear. In some cases, there may be drainage or bleeding.
- Nasal Symptoms: Common indicators include nasal discharge, pain, or bleeding from one nostril. Children may exhibit signs of distress or discomfort.
- Throat Symptoms: Patients may report difficulty swallowing, choking sensations, or persistent coughing. In severe cases, there may be signs of airway obstruction.
- Eye Symptoms: Symptoms can include redness, tearing, or a sensation of something being in the eye. Patients may also experience blurred vision or pain.
Importance of Timely Diagnosis
Prompt recognition of these symptoms is crucial, as delays in treatment can lead to complications such as infections, tissue damage, or airway obstruction. If a foreign body is suspected, seeking medical attention is essential.
Methods of Foreign Body Removal
Techniques Used in General Practice
The approach to foreign body removal depends on the object’s location, size, and type. General practitioners are equipped with various tools and techniques to facilitate safe removal.
-
- Ears: Common methods include:
- Suction: Gentle suction can effectively remove soft or graspable objects.
- Forceps: For larger or more accessible items, forceps may be used to grasp and extract the foreign body.
- Irrigation: In some cases, warm water may be used to flush out the object.
- Nose: Techniques for nasal foreign body removal include:
- Direct Visualization: Using forceps or hooks to grasp the object.
- Positive Pressure: Instructing the patient to blow their nose while blocking the opposite nostril can sometimes expel the object.
- Balloon Catheter: A lubricated catheter can be used to push the foreign body forward for easier removal.
- Throat: Removal of throat foreign bodies often requires more advanced techniques:
- Endoscopy: Flexible or rigid endoscopy may be necessary for visualization and extraction.
- Surgical Intervention: In cases of complete airway obstruction, immediate surgical consultation is required.
- Eyes: For foreign bodies in the eye, methods include:
- Flushing: Rinsing the eye with saline solution to remove small particles.
- Cotton Swabs: Carefully using a swab to remove larger objects, if visible.
- Ears: Common methods include:
Considerations for Safe Removal
When performing foreign body removal, healthcare providers must consider several factors, including the patient’s age, cooperation level, and the potential for complications. In some cases, referral to a specialist may be necessary.
Risks and Complications
Potential Complications from Delayed Removal
Failure to promptly address foreign body incidents can lead to various complications, including:
-
- Infections: Retained foreign bodies can become a source of infection, leading to abscess formation or systemic illness.
- Tissue Damage: Prolonged presence of a foreign object can cause irritation, inflammation, or necrosis of surrounding tissues.
- Airway Obstruction: In cases involving the throat, delayed removal can result in choking or respiratory distress.
Importance of Professional Intervention
Given the potential risks associated with foreign body retention, it is crucial to seek professional medical assistance as soon as symptoms arise. General practitioners are trained to assess the situation and determine the appropriate course of action.
When to Seek Medical Help
Recognizing Emergency Situations
Certain scenarios warrant immediate medical attention, including:
-
- Choking: If a foreign body is suspected to be obstructing the airway, calling emergency services is essential.
- Severe Pain: Intense pain or discomfort that does not subside may indicate complications requiring urgent care.
- Inability to Swallow: Difficulty swallowing or breathing should be treated as a medical emergency.
Routine Visits for Non-Emergency Cases
For less urgent situations, such as a foreign body lodged in the ear or nose without severe symptoms, scheduling an appointment with a general practitioner is advisable. Early intervention can prevent complications and ensure safe removal.
Preventive Measures
Educating Patients and Caregivers
Preventing foreign body incidents, particularly in children, involves education and awareness. Caregivers should be informed about the risks associated with small objects and the importance of supervision during playtime.
-
- Age-Appropriate Toys: Selecting toys that are suitable for a child’s age can reduce the likelihood of foreign body incidents.
- Safe Storage: Keeping small items out of reach of young children can help prevent accidental ingestion or insertion.
Awareness of Personal Habits
Adults should also be mindful of their habits, such as using cotton swabs in the ears or engaging in risky behaviors that may lead to foreign body incidents. Awareness can significantly reduce the risk of such occurrences.
Foreign body removal is a critical service provided in general medical practices, addressing a range of situations where objects become lodged in the body. Understanding the types of foreign bodies, recognizing symptoms, and knowing when to seek help are essential for ensuring timely and effective treatment. By promoting awareness and preventive measures, healthcare providers can help reduce the incidence of foreign body-related emergencies.
Our Medical Memberships Cover Foreign Body Removal
Direct Primary Care (DPC) is a model of care where the patient pays an upfront monthly membership fee for high-quality and low-cost primary care. This means no surprise fees or being billed differently for sick visits versus wellness visits. This model is accessible to all. The focus of Direct Primary Care is ongoing wellness and prevention to prevent unnecessary hospitalizations or costly visits to the ER for primary care services.
> Learn More About Our Medical Memberships
Contact Us (727-312-1262) To Learn More!
—
 About Honeybee Holistic Health
About Honeybee Holistic Health
Honeybee Holistic Health strongly believes in a holistic, organic, and integrative model of care where the patient is the center of all decisions. Our approach is to empower each one of our patients to heal themselves and to make informed, autonomous decisions in their plan of care. This is approached by integrating modern medicine with well-studied homeopathic treatment options when appropriate.
> Learn More